Introducing mirrord for CI
We’ve launched mirrord for CI, which uses mirrord to enable running concurrent CI tests on a shared, production-like Kubernetes environment. In this blog we’ll cover the problems with traditional CI, what mirrord for CI is, and how you can get started with it.
Why traditional CI pipelines slow developers
Testing cloud native applications isn’t an easy task because of their distributed nature. A code change made on a single service often requires other services to be brought up as well to test how it would behave. Today organizations do this in CI pipelines by either spinning up ephemeral cloud environments or using local Kubernetes tools like minikube and kind in their pipelines. Both approaches have their own set of drawbacks:
Ephemeral cloud environments in CI: Spinning up a cloud environment or deploying to an existing environment for each CI run significantly slows down developers, since every change can mean waiting 20–30 minutes for the environment to spin up, container images to build, and get deployed. On top of that it’s expensive and operationally heavy, increasing cloud costs and adding ongoing maintenance work for platform teams. These environments also rarely mimic a full production-like setup because they run with limited data, lack access to third-party APIs, and often don’t include all microservices when systems are large.
Local Kubernetes tools: To save costs, some organizations replace cloud environments with tools like minikube and kind, which let them create a Kubernetes cluster local to the CI runner for testing purposes. The drawback here being that local clusters behave very differently from real ones, which means poor test coverage. On top of that, this also takes time and isn’t necessarily cheap, since you need to run your pipelines on machines powerful enough to support local clusters, so your CI bill is higher.
What is mirrord for CI?
These problems don’t only apply to CI, but also to local development - local Kubernetes tools are resource-intensive and don’t simulate production, and personal cloud environments are incredibly expensive. mirrord already fixes those by allowing developers to run their local code in the context of a shared Kubernetes environment (usually the staging cluster) and mirror traffic, files, and environment variables between the two. mirrord for CI extends this functionality to CI pipelines as well. With mirrord for CI:
- Your code, i.e. the microservice in the branch you want to merge, runs in the CI runner, but mirrord proxies incoming and outgoing traffic, environment variables, and files back and forth between it and the cluster.
- The result is that your service in the CI runner behaves as if it’s running in the cloud, allowing you to test it against real services, real data, and real traffic, without spinning up or deploying anything, easily saving 20–25 minutes per CI run.
- mirrord lets you connect to an existing Kubernetes environment (like your staging or pre-prod cluster), removing the need to spin up dedicated ephemeral environments for CI, reducing your cloud bill significantly.
If you’re not familiar with mirrord, this might sound a bit too good to be true. The obvious question is how can multiple CI runners safely connect and run tests on an existing Kubernetes cluster which other developers might also be using for development or testing? What sets mirrord apart is its ability to provide isolation within the shared cluster for each run. Features like HTTP traffic filtering, database branching, and queue splitting ensure that CI runners’ traffic and data are isolated, without affecting other runners or developers using the shared environment. You can also use features like mirrord Policies, which act as guardrails preventing unsafe operations on the shared cluster.
How to get started
mirrord for CI is available for mirrord users on the Enterprise plan. To use mirrord for CI, you’ll first need to generate an API key:
mirrord ci api-key
Copy the generated key and save it as a secret environment variable named MIRRORD_CI_API_KEY in your CI provider.
Starting a mirrord CI session
The mirrord ci start command is used to start the service being tested in your CI runner, and supports the same arguments as mirrord exec, including specifying a target with --target or using a configuration file with --config-file. Here’s an example for starting a Go service called ip-visit-counter:
mirrord ci start --target deployment/ip-visit-counter go run ip-visit-counter.go
At this point, your microservice will be running inside the CI runner and mirrord will be connecting it to the cluster. You can now run your test script as usual. These tests can target the stable, already deployed service in your cluster (for example, the service running in staging). mirrord will intercept that traffic and redirect it to the service running inside the CI runner, allowing it to work against real dependencies without deploying anything.
Note: Make sure to run
mirrord ci stopafter the tests finish running.
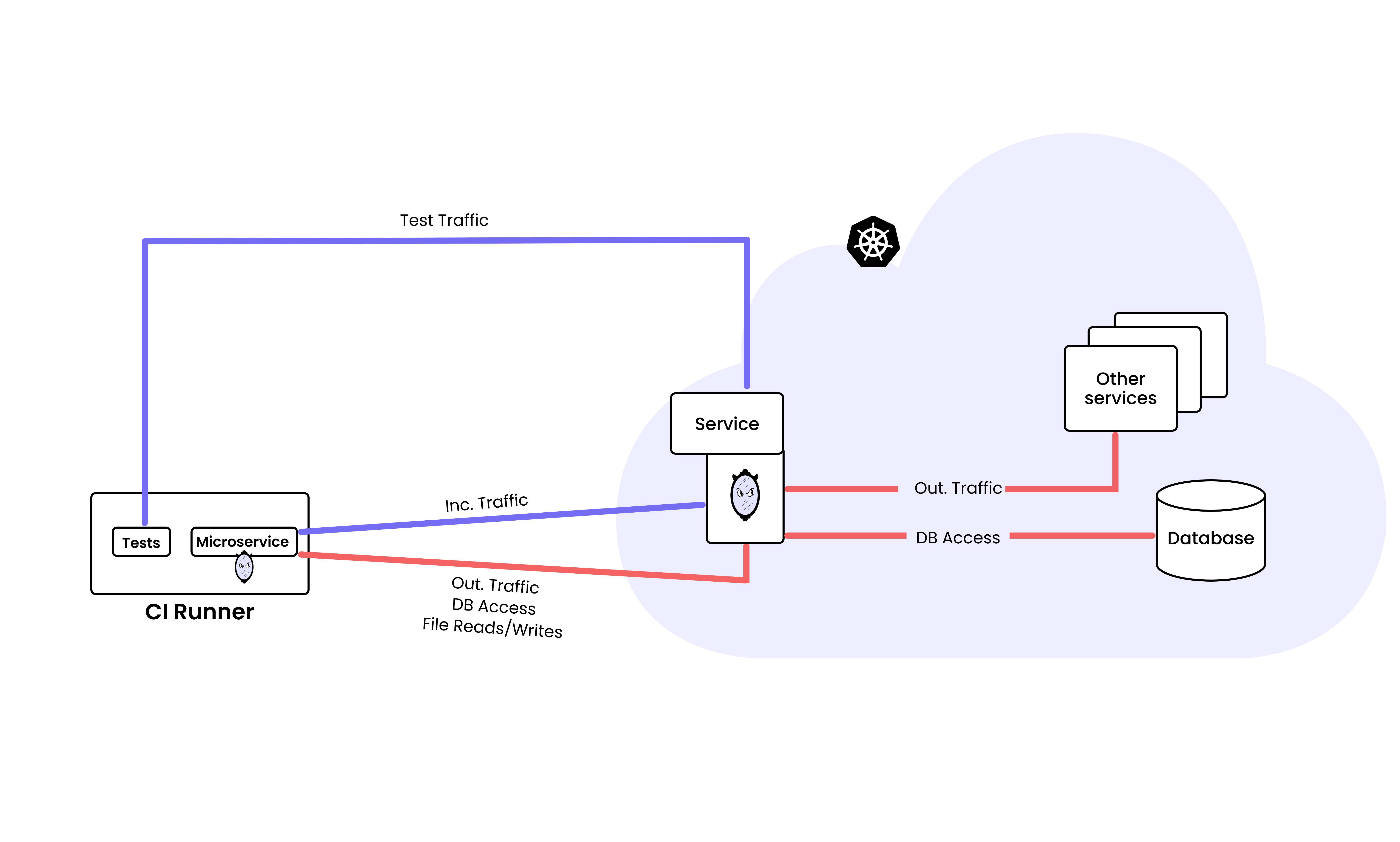
How mirrord for CI works
CI platform support
mirrord for CI works with all major CI providers, including GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, CircleCI, and others. As long as you can install the mirrord CLI and set environment variables, it will work.
Below is a simple example of how to use mirrord for CI in GitHub Actions:
name: Test with mirrord for CI
on:
pull_request:
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
MIRRORD_CI_API_KEY: ${{ secrets.MIRRORD_CI_API_KEY }}
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Install mirrord
run: |
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metalbear-co/mirrord/main/scripts/install.sh | bash
- name: Run tests with mirrord for CI
shell: bash
run: |
mirrord ci start --target deployment/ip-visit-counter go run ip-visit-counter.go
npm test
mirrord ci stop
With this setup, the tests you’ve defined to be executed when running npm test can use the staging endpoint where your service is deployed, and mirrord will mirror requests sent to that staging endpoint to the service running in the CI runner. The service will then still have access to staging for any downstream logic (e.g. accessing a database). This lets you see how the code in your pull request would behave in a production-like environment without you having to provision new infrastructure or build and deploy images.
Don’t let your team suffer through slow CI
Traditional CI pipelines force teams into slow, expensive workflows that still fall short of realism. mirrord for CI fixes this problem by running the PR code inside your CI runner while connecting it to an existing Kubernetes environment. This way you get fast feedback, realistic tests, and no extra infrastructure to manage. No ephemeral environments to spin up, no images to build and deploy, and no special CI-only setups to maintain.
If you want to see this in action you can book a call with us and in just 30 minutes, we’ll show you exactly how mirrord eliminates your CI bottleneck and fits into your existing setup.

